Followup Payment
Via Phone, Email, SMS, Whatsapp
Exception-based receivables management
Collect Payments
Cash, Cheque, DD, NEFT, CC, DC
Customer portal/chatbot todo payments
Send Receipts
Via Email, SMS, Whatsapp
Real-time customer payment data
Reconcile Party
Intelligent Invoice matching
Credit agency integration/Reduce DSO
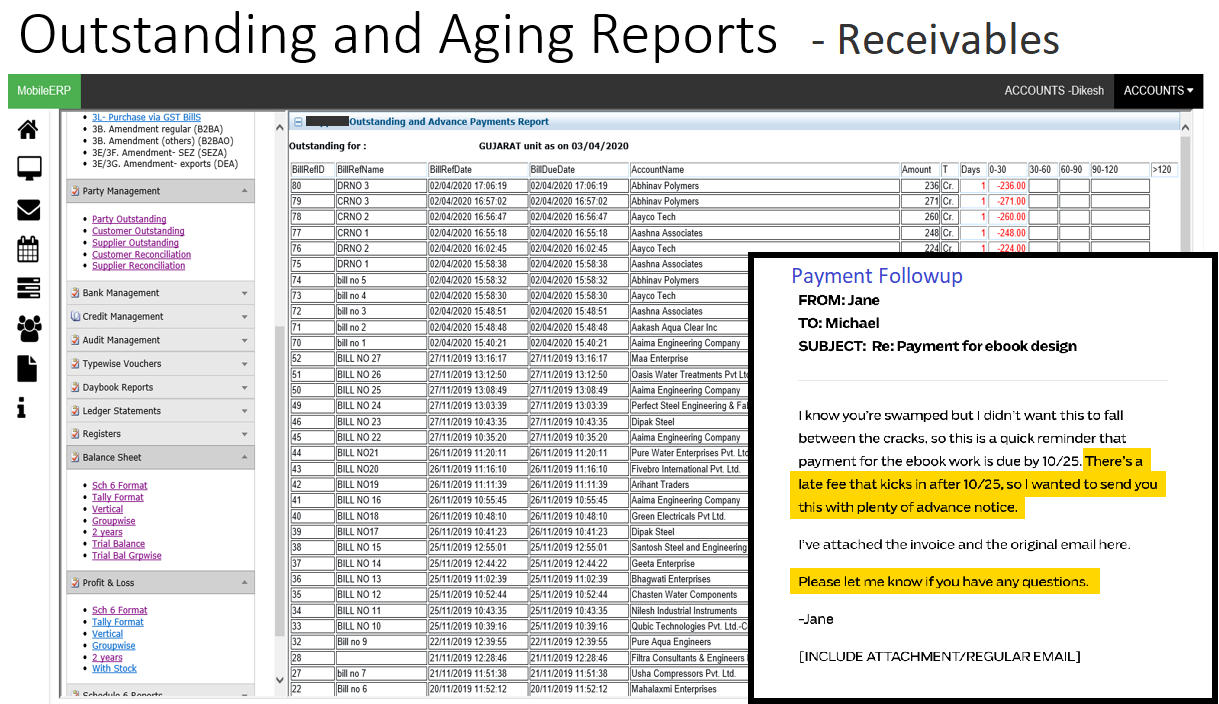
Followup
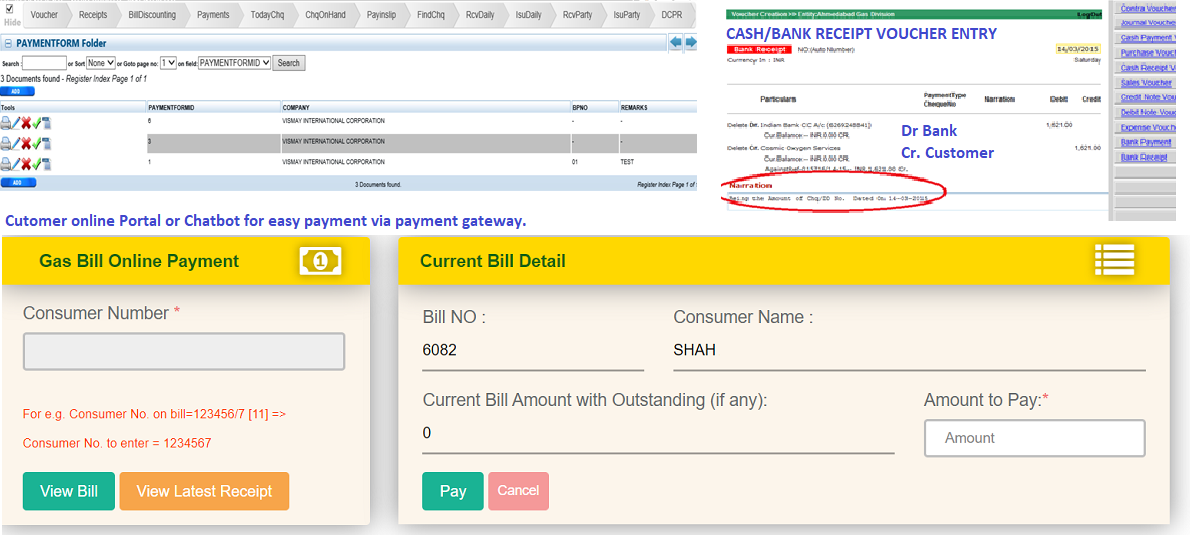
Collect
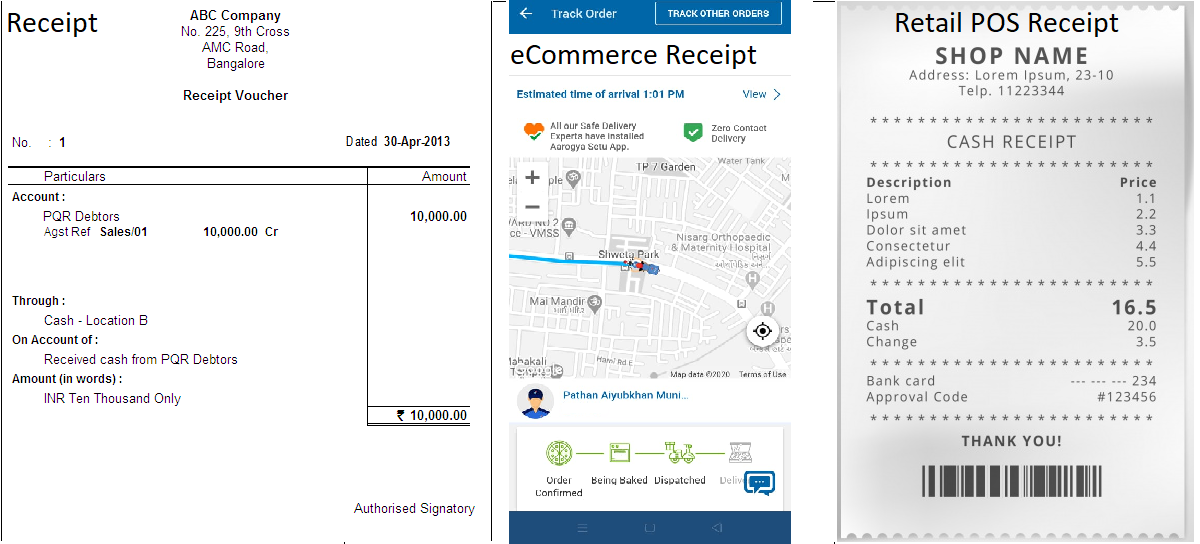
Send
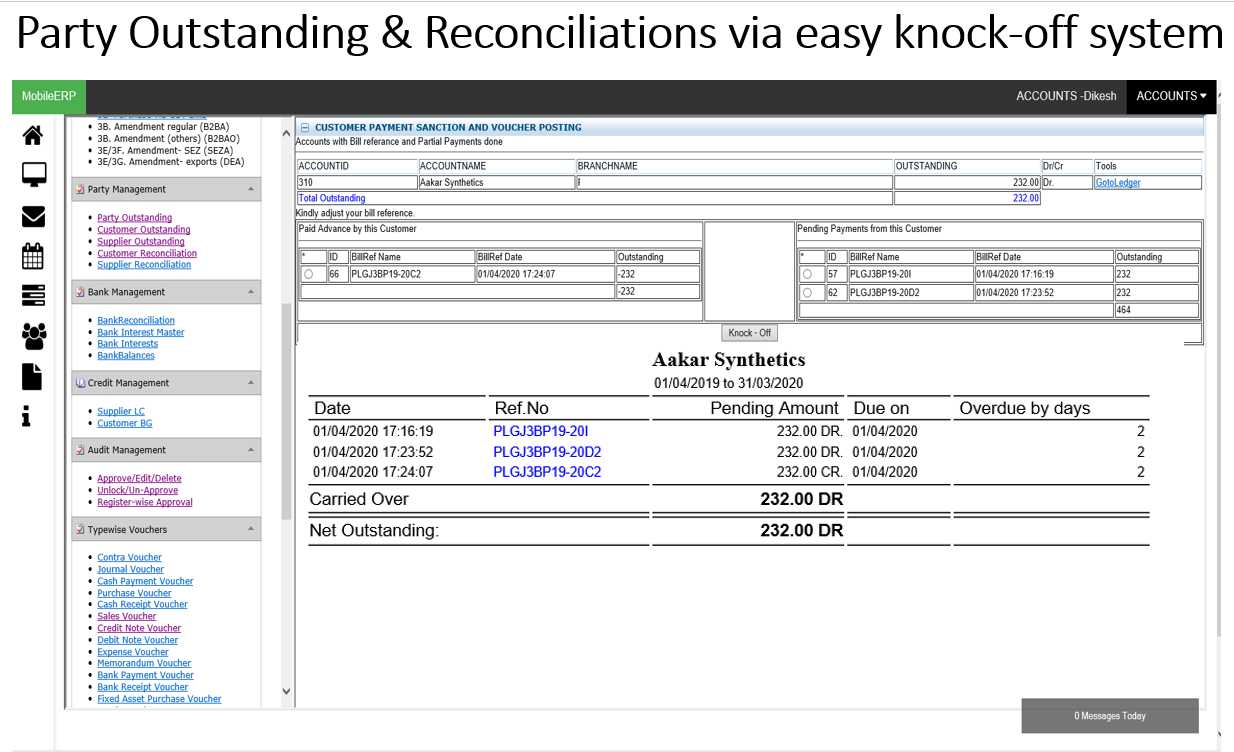
Reconcile
What is Receivables Management?
Receivables management is professional dunning, with the goal of avoiding payment defaults and ensuring the long-term liquidity of a company. It is part of the internal accounting department and begins with arranging, recording and organising outstanding payments. ... This is also referred to as debtor management.Put simply, Receivable Management or Managing Accounts Receivables means collecting the payments due for Sales in a timely manner. When we sell any services, products or solutions to our clients or customers, they owe us the money. Collecting that money is called Receivables Management.
What are the five steps in managing accounts receivable?
According to the text, below are the five steps to managing accounts receivable:1. Determine to whom to extend credit.
2. Establish a payment period.
3. Monitor collections.
4. Evaluate the liquidity of receivables.
5. Accelerate cash receipts from receivables when necessary.
How do you reduce accounts receivable?
How to Minimize Accounts Receivable and Increase Cash Flow1. Implement upfront fees. Many accounting firms charge their clients upfront fees. ...
2. Structure payment plans. After you receive an upfront fee, connect with your clients to set up a payment plan for the remaining balance. ...
3. Stick to payment deadlines and do rigorous payment followup with clients...
4. Provide customer various methods to do quick payments via Website, MobileApp, Chatbot, Bank, COD, Credit Cards, Debit Cards, Payment gateway etc..
What is Revenue Recognition?
The revenue recognition principle, a feature of accrual accounting, requires that revenues are recognized on the income statement in the period when realized and earned—not necessarily when cash is received. The revenue recognition principle states that one should only record revenue when it has been earned, not when the related cash is collected. Before revenue is recognized, the following criteria must be met: persuasive evidence of an arrangement must exist; delivery must have occurred or services been rendered; the seller's price to the buyer must be fixed or determinable; and collectability should be reasonably assured.According to the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB), the purpose of revenue recognition is “to report useful information to users of financial statements about the nature, amount, timing, and uncertainty of revenue from contracts with customers.”
The accrual journal entry to record the sale involves a debit to the accounts receivable account and a credit to sales revenue; if the sale is for cash, debit cash instead. The revenue earned will be reported as part of sales revenue in the income statement for the current accounting period.
In general, the revenue recognition process can be used to perform these tasks:
1. Allocate revenue, to help guarantee that the appropriate revenue price is recognized, based on the value of the components on multi-element orders.
2. Defer revenue, based on a revenue schedule that represents the contractual time frame and percentages for recognizing revenue over time.
The Revenue recognition feature provides a flexible framework that lets you define company-specific rules for recognizing both the revenue price and the revenue schedule.
Released products are used to support revenue recognition on sales order documents. The released products contain the setup that is required to determine the revenue price and the revenue schedule. The sales order can originate from a Time and materials project.
What is Revenue Schedule
A revenue schedule represents how revenue amounts from a single charge are distributed over time and recognized in accounting periods. Revenue schedules maintain consistency with the currency used.Companies can use the revenue schedule functionality without using the revenue price functionality. Therefore, the price on the sales order lines will be used as either revenue or deferred revenue. If a revenue schedule exists on the sales order line, the price on the sales order line will be deferred. If a revenue schedule doesn't exist on the sales order line, the price on the sales order line will be posted to a revenue account when it's invoiced.
The revenue price is calculated either when the sales order is confirmed or when the invoice is posted. To preview the revenue price before the invoice is posted, you must confirm the sales order.
When the sales order is confirmed, an expected revenue schedule is also created if any sales order line has a revenue schedule. When the sales order is invoiced, the expected revenue schedule is deleted, and the expected revenue schedule is replaced with the actual revenue recognition schedule.
What is Deferred Revenue or Advance Payment?
Deferred revenue is the portion of a company's revenue that has not been earned, but cash has been collected from customers in the form of prepayment or advance payment. All payments needs to be adjusted against specific invoice during Party Reconciliation process.What is bill of exchange?
A bill of exchange is a written or electronic order from a customer that specifies that another party, usually a bank, should pay a stated amount to the company. When you use a bill of exchange as payment for a sales order invoice or free text invoice, you credit the customer account. That credit is secured by the bill of exchange until the customer pays the bill of exchange to the bank. Typically, you will settle the invoice with the bill of exchange on the due date. When you receive notification from your bank that the bill of exchange has been honored, you can close the bill of exchange. You can draw a bill of exchange through your bank at either of the following times:1. On the due date. This approach is known as remit for collection.
2. Before the due date, typically on the discount date that is specified in the terms of payment that are set up for the customer. When you post the transaction, the discount amount is posted to an expense account. The remaining amount is a liability to you until the bank receives payment from the customer. This approach is known as remit for discount.
What is Bill Discounting?
Bill discounting, or invoice discounting is the act of sourcing working capital from future payables. ... Bill discounting can be defined as the advance selling of a bill to an intermediary (an invoice discounting business) before it is due to be paid. This results in less administrative charges, fees and interest. The bills or invoices under bill discounting are legally the 'bill of exchange'.For example: You have sold goods to Mr. X, he has given you letter of credit from bank of 30 days, if you want to get money from bank before 30 days, the bank will charge some interest rate from you, which in return will be called as discount for the seller.
What is receipt of payment?
A payment receipt, also referred to as a receipt for payment, is an accounting document that a business provides its customer as proof of full or partial payment toward a product or service. Payment receipts typically include the following information about the transaction: Business name.What is customer payment Insight?
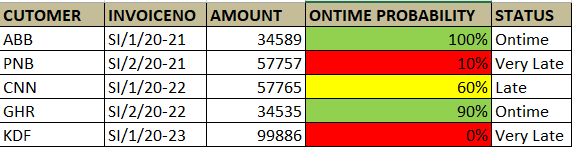
Using a machine learning model, which leverages historical invoices, payments and customer data, Customer payment insights (Preview) more accurately predicts when a customer will pay an outstanding invoice.For each open invoice, Customer payment insights (Preview) predicts three payment probabilities:
1. Probability of payment being made on time
2. Probability of payment being made late
3. Probability of payment being made very late
To help Organizations understand the total payment amount they can expect from a customer in one of the three buckets, On time, Late and Very late, Customer payment insights (Preview) also provides an aggregated view of expected payments.
Also, each invoice is assigned a probability of payment on time. If the probability of payment on time is less than 50%, the invoices are tagged with a red circle to indicate that these invoices may require collections attention.
Customer Payment Insights (Preview) also provides contextual information to explain the prediction, such as the top factors that influenced the predictions, the current state of business with the customer, and details about the historical customer payment behavior. In many businesses, the collections process has been a reactive activity; the collections process doesn’t start until invoices come due.
With Customer payment insights (Preview), organizations can be more proactive about collections. They no longer have to wait for the transactions to become due to start the collection process. Instead, they can use the payment prediction capability to determine whether proactive collections will improve the probability of being paid on time. Payment prediction also gives businesses the information needed to justify starting the collection process early.
What is Collection Sales Target?
The Coolection Sales Target KPI measures current sales revenue and compares that to a target or past performance. The sales target can be set as either a monetary value, number of units sold, or number of accounts. ... One of the keys of setting a sales target is ensuring it's visible to the entire team.To set achievable collection sales targets, a few things are important:
Revenues. Determine what revenues are required for the business to succeed.
Be realistic about timelines. ...
Sales people meetings. ...
Incentivise your sales team properly. ...
Ensure that the sales team is managed and monitored. ...
Reporting system. ...
Collection analysis.
When to Hire a Collection Agency?.
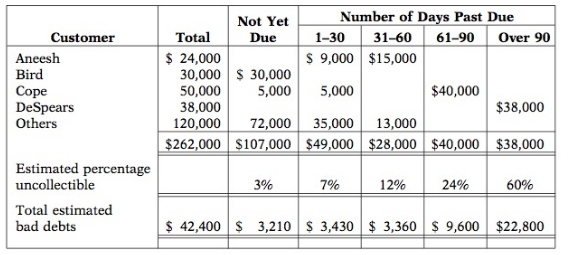
When it comes to collecting outstanding debt, generally, the more time that passes, the lower chance you have of recouping the money. Most companies send past-due accounts to a collection agency when they are 90 to 120 days past due.How to send Payment Reminders via Collection Letters or Emails
Collection letters are set up at the transaction level, multiple letters might be generated for a customer, based on transaction aging. Therefore, an individual customer might receive, for example, one collection letter for transactions that are 30 days overdue and another collection letter for transactions that are 90 days overdue. The single collection letter will contain all the transactions that are overdue for the customer. Because the grace days are now tracked at the customer level, the next collection letter won't be sent until the number of grace days has passed for the next collection letter in the sequence, even though transactions became overdue after the last collection letter was sent. This option helps reduce the number of collection letters that you must send to each customer.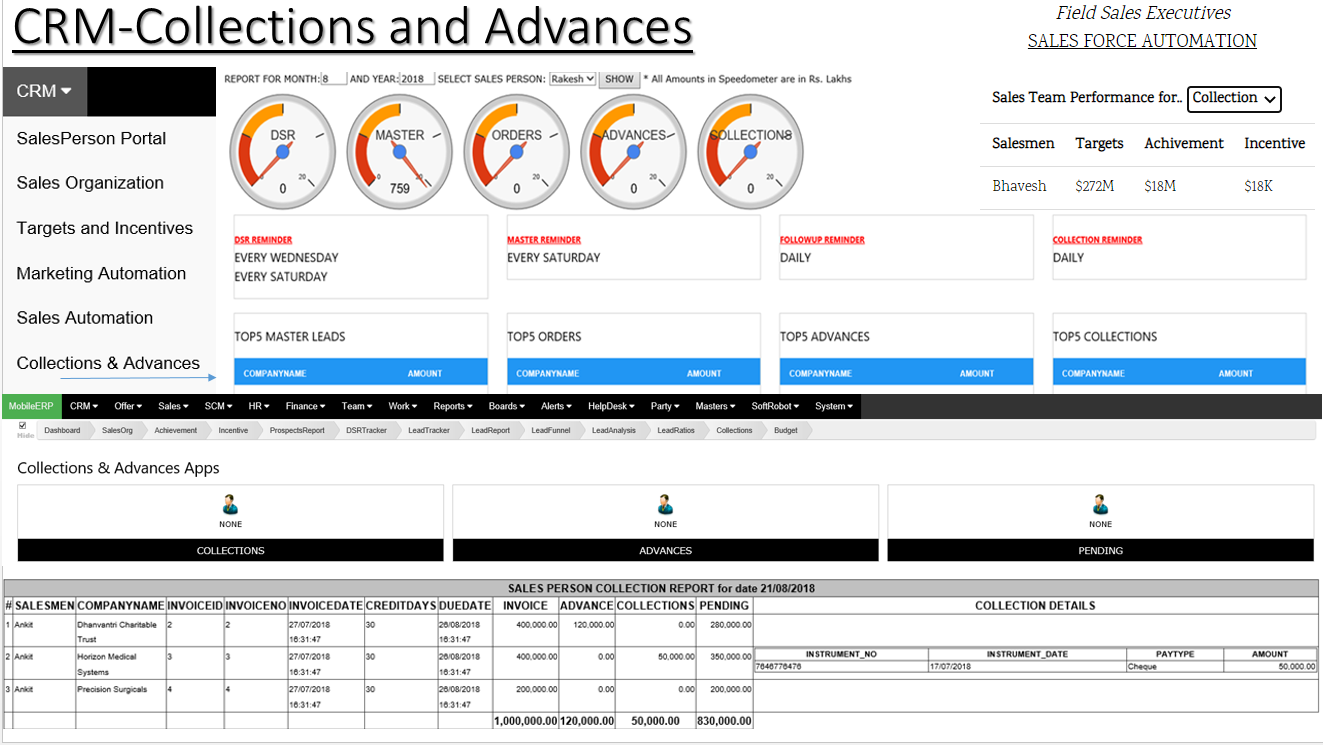
How to calculate Interest on Late Payments?.
You can set up a single interest code and apply it to multiple customer posting profiles, billing codes, or to specific invoice lines. When the interest code details are changed, all features that use the code will automatically implement the changes on new transactions. For each interest code, you can set up two types of rates:a. Rates for interest earnings − These represent revenue that is earned by charging interest on invoices or interest notes.
b. Rates for interest payments − These represent a cost that is paid for interest on credit notes.
Both of these rate types can exist at the same time and in the same interest code. Interest rates can be based on three calculation types:
1. Interest by percentage: e.g. 1 percent interest for every months that the invoice payment exceeds the transaction due date.
2. Interest by amount.e.g. e.g. Fixed Interest Amount of $500.00 for every 30 days that the invoice payment exceeds the transaction due date.
3. Interest by range, which results in a single percentage or amount.
3a. By Percentage Range: The interest value will be 1 percent for invoice amounts up to 1,000.00, 2 percent for amounts from 1,001.00 to 5,000.00, and 3 percent for amounts larger than 5,000.00.
3b. By Amount Range: The interest value will be $5.00 per 15 days during the first 60 days, $35.00 per 15 days during days 61 to 90, and $50.00 per 15 days from day 91 and after.
3c. By Months Range: 1 percent per month for the first three overdue months, 2 percent per month for the second three months, and 3 percent per month for each month beyond the first six months.
When an interest code is used to calculate interest, a separate interest note is created for each interest rate that is in effect during the time that the payment has exceeded the transaction due date. You use the Earnings tab on the Interest code page to set up interest rates for interest that you earn by charging interest. Use the Payments tab to set up interest rates for interest that you pay.
Waive, reinstate, or reverse interest fees
1. Waived charges are forgiven. You might waive a charge if, for example, a customer disputes the charge, and you want to maintain a good business relationship with that customer.
2. Reinstated charges become due again. You can reinstate charges that were previously waived. You might have to reinstate charges if you determine that they should not have been waived.
3. Reversed charges are removed from a customer’s account and are no longer due. You might reverse charges if, for example, the wrong interest rate was selected to calculate the amount that a customer owes. You can use a separate process to recalculate interest and create an interest note that contains new charges for the customer.
